Worms are representatives of lower worms that live in the human body. A disease associated with human infection by various types of worms is called helminthosis. This disease is not uncommon and occurs among certain segments of the population. Children are susceptible to pinworm infection, hunters - trichinella, fishermen and lovers of Japanese cuisine (raw fish in the form of sushi) suffer from diphyllobothriasis.
Many diseases, paradoxically, can occur in the human body due to helminthosis. Today, the theory of the connection between cancer and parasitic infections is one of the most relevant. In the case of helminthosis, symptoms are not always visible, and despite this, if patients with this disease experience any unpleasant and uncomfortable feelings, they are considered as symptoms of other diseases. The patient has been treated for pancreatitis, gastritis or colitis for years, he does not suspect that the cause of his diseases is helminthosis.
How does the infection occur?

Infection with helminths occurs as follows:
- Through unwashed hands
- When in contact with the ground
- After an insect bite
- For dirty hands
- When eating raw meat and fish
- After eating unwashed fruits and vegetables
- After contact with an animal
- After contact with infected people
Adult parasite eggs can be found in soil, water and food (raw and undercooked meat or fish). Rare cases of the disease occur due to insect bites. The mechanism of infection with helminthosis is oral-fecal. Humans ingest parasite eggs through food and water. Contact and domestic methods of infection also occur. It occurs when hands are not washed thoroughly after contact with soil or sand.
Vegetables and berries grown in the soil, which are not washed enough, are also a source of worm infection. Children playing in the yard and with pets are at risk of getting worms. Pets roaming freely on the streets can bring home helminth eggs. Flies and other insects, after contact with animal feces, can easily transfer helminth eggs by landing on food. Surprisingly, human-to-human transmission is also possible. It happens like this: the female pinworm can crawl through the intestines and lay eggs directly on underwear, causing severe itching. After a person scratches the itchy area, it can come into contact with other toiletries and household items. These items get into the hands of other family members, after which they become infected.
Waterborne infection is also possible. Many parasite eggs easily fall into open reservoirs and wells. Drinking unboiled well water is extremely dangerous.
Types of helminthiasis
Helminths differ in the way they penetrate the human body:
- Biohelminths
- Geohelminths
- Infectious
Biohelminths are transmitted to humans through contact with animals. Geohelminths can be transmitted through soil. Contagious ones are caused by contact with an infected person. The disease manifests itself differently depending on the method of infection, the number of worms and the degree of adaptation in any human body.
Stages of helminthiasis
The most destructive effect on the body is caused not by adults, but by their larvae. Adults have already chosen a comfortable place for themselves in the human body, and the larvae pass through the organs and leave their lesions behind. The most common place where parasites live is the gastrointestinal tract. Different types of parasites prefer different habitats. Thus, roundworms are located in the small intestine, and pinworms are located in the large intestine and lower parts of the small intestine. According to the habitats of the parasites, helminth infections are as follows:
- Transparent
- Cloth
Luminal ones are located in the lumen of the genital organs, and tissue ones are located inside the tissues. Depending on the growth, the parasites can change their habitat, passing from the luminal form to the tissue form. Helminthosis develops in two stages:
- spicy
- Chronic
The acute phase lasts from a week to a month, and the chronic phase lasts until treatment. The acute phase begins with the introduction of the egg and continues with the maturation and growth of the parasite. The disease manifests itself as an allergic reaction to a foreign organism. In the chronic stage of the disease, various reactions of the body occur. During this period, the parasite moves throughout the body in search of shelter. The disease is accompanied by disturbances in the work of organs and systems in the human body. By integrating into the immune system of the human body, parasites consume substances necessary for growth and development. This causes disruption of metabolism, disruption of the digestive system, and difficulty in the assimilation of vitamins and minerals.
In addition to this damage, parasites poison the body by pouring their waste into the human body, causing intestinal disorders, decreasing immunity, and causing bacterial infections. Parasites increase the risk of developing cancer. This happens due to the negative effect on the immune system and the stimulation of cell division. Often, a patient is examined by many specialists who find many diseases. And in this case, a doctor - a parasitologist can replace all specialists.
Classification of helminths
Types of worms in humans:
- Flatworms
- Roundworms
Flatworms include:
- Trematodes (opisthorchiasis, schistosomes, paragonimus)
- Cestodes (broad tape, pork, echinococcus, alveococcus)
- Roundworms or nematodes:
- Pinworm
- Ascaris
- corn
- Trichinella
This classification of helminths is presented in the medical literature. In order to successfully solve a problem such as helminthiasis, it is necessary to study in depth the characteristics of the structure and life cycle of parasites.
Trematodes
Another name for trematodes is flukes. These parasites are flat leaf-shaped or lanceolate with two suckers. One sucker is located in the mouth, and the second is in the peritoneum, which serves for closure. All representatives of flukes enter the body through an intermediate host. Most of these parasites are hermaphrodites.
Opisthorchosis
It is a worm up to 1. 3 cm long with two suckers. Opisthorchiasis is a hermaphrodite that parasitizes the liver, gall bladder and pancreas in humans and some carnivorous animals (fox, dog, cat). Opisthorchosis eggs come out of the human or animal body with feces. When these eggs enter the body of water, they are swallowed by freshwater molluscs, inside which the larvae hatch and develop. The process of development and maturation of larvae lasts for two months. Then the larvae crawl out of the mollusk and penetrate the skin of the carp. After six weeks, the larvae turn into full-fledged adult parasites. Opisthorchosis enters the body of an animal or person after eating contaminated fish. This worm can live in a living organism for up to 20 years. Symptoms of opisthorchosis:
- Allergy
- Weakness
- headache
- Dizziness
- Depression
- Loss of consciousness
Damage caused by opisthorchosis to the body:
- Poisoning by parasitic waste products
- Liver tissue damage
- Damage to the gallbladder
- Bile flow disorder
- Inflammation of the pancreas
- Secretory dysfunction
- Decreased gastric motility
- Thickening of the walls of some organs, resulting in tumors.
The chronic course of the disease is characterized by the following:
- Heaviness after eating
- Pain
- Vomiting
- nausea
Prevention of infection: To avoid infection with opisthorchiasis, you should not eat raw fish. Larvae die during heat treatment of products. Dried fish can be eaten only if it has been previously salted. Also, if the fish is frozen for a long time, the larvae die.
Schistosomes

These parasites are of different species, they look like needles with a length of 0. 4-2. 6 cm. Females are longer and larger than males, and lay up to 3, 000 eggs per day. The method of reproduction is the same as the previous type of parasite through freshwater molluscs. The larva enters the human body through the skin and mucous membranes while swimming in freshwater. It can also enter the body of a person who accidentally swallows water while swimming. After a day, the larva turns into an adult and enters the peripheral vessels, through which it is sent to the lungs and venous vessels. There, the schistosome reaches sexual maturity.
Schistosoma lays its eggs in the intestines, mucous membranes and bladder. Eggs are removed from the human body with urine or faeces and begin the development process again. Schistosoma lives in the human body for several decades, causing damage and infecting new individuals. The problems caused by infection with schistosomes are not caused by adults, but by their eggs. Only half of the eggs are excreted from the body, the rest accumulate in the organs. The eggs of this parasite contain spines that damage human internal organs, often causing ulcers in the infected person. Patients with schistosomiasis have the following symptoms:
- Appetite disturbance
- Anemia
- Enlarged liver
- The spleen changed
- Decreased intestinal motility
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Lose weight
- Intestinal bleeding
- Pain during urination
- Allergies
- Weakness
When the genitourinary system is infected, patients experience the following:
- Menstrual disorders and miscarriages in women
- Impotence and incomplete ejaculation in men
If eggs enter the central nervous system:
- Acute cerebral schistosomiasis
- Chronic brain injury
- Death
In infected children, growth and development are delayed, and their performance at school decreases. Prevention includes avoiding swimming and avoiding walking barefoot in tropical waters.
My paragon

Paragonium is a 1 cm long lungfish with an egg-shaped body and red spines. This parasite multiplies in the lungs of animals and enters the human body by feeding on crayfish and freshwater crayfish. The parasite affects the respiratory system. Patients with paragonimiasis are characterized by allergic reactions and reduced immunity. Symptoms:
- Temperature rise
- Cough
- Sputum production from the lungs during coughing
- Shortness of breath
- In severe cases, the sputum contains blood and parasite eggs
- Wheezing is clearly heard in the patient's lungs
Prevention: Avoid eating raw crayfish and crabs.
Cestodes
Representatives of cestodes are tapeworms of various lengths. Some parasites reach gigantic sizes. These parasites have suckers, hooks or suction slits on their heads. Parasites need these devices to attach to the intestinal walls. Cestodes affect the whole human body, the most dangerous for children who quickly develop anemia.
Echinococcus
These parasites reach a length of 5 cm and are the causative agents of Echinococcus disease. A multi-chambered representative of this type of worms is the causative agent of a disease such as alveococcosis. The disease is carried by cattle and domestic animals. When caring for these animals, parasite eggs fall into people's hands from their fur. When parasites enter the human intestine, they bite into the mucous membrane. As the parasite matures, 4 compartments are formed, the last compartment is filled with eggs. These sections break off and spread throughout the body, infecting it. The fourth division scatters the eggs all over the body.
The patient's infected organ, for example, the liver, enlarges. Suppuration may occur. An enlarged organ can even rupture the abdominal cavity. And this can lead to serious sepsis of the body and even death. Symptoms:
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Allergic reactions to waste products of parasites.
Echinococcus affects:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Eyes
- Thyroid gland
- Liver
- Lungs
- uterus
This parasite can cause tumors, including malignant ones. The most unpleasant thing is that the treatment of this disease is possible only through surgery. Prevention: personal hygiene when in contact with animals.
Nematodes
These worms with a round or cylindrical elongated body are most common parasites in children's bodies. These roundworms include pinworms, roundworms, and hookworms.
Pinworms
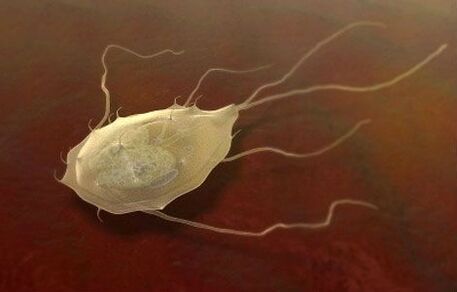
These are small white worms. The length of the female is 1 cm, the length of the male is 0. 5 cm. These parasites have pointed tails, so they were called pinworms. Pinworms live in the human intestine. At the front end of the parasite, there is a sucker, with the help of which the pinworm digs into the intestines, and the sharp end hangs in the lumen and damages the walls. This disease is called enterobiosis. You can get infected from a person through dirty hands. The disease is observed in preschool children who go to kindergarten. A symptom of pinworm infection is itching near the anus. More often itching is felt at night, when the female lays eggs that secrete a special substance. Symptoms:
- itching
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- headache
- Loss of appetite
Prevention: hand washing.
Roundworms
These worms are the largest. The length of the female is up to 0. 5 m. The female lays 200, 000 eggs a year, regardless of the male. The mechanism of infection is fecal-oral. Ascaris eggs enter the human body through dirty hands along with unwashed vegetables and fruits. Entering the intestine, the larva is selected from the shell and penetrates the intestinal walls, migrates from the intestinal veins to the liver, from the hepatic veins to the heart, through the pulmonary arteries to the bronchi, then to the trachea and into it. Mouth. Some of the larvae die in the open air, the rest are swallowed back. Symptoms:
- nausea
- Vomiting
- Jaundice
- Pancreatitis
- Frequent acute respiratory infections
- Bronchitis
- I have pneumonia
Prevention:
- Hand washing
- Washing vegetables and fruits
- Observance of personal hygiene rules
- Protect food from flies, cockroaches and other carriers.
In conclusion, we can say that the cause of the disease is not always bacteria and viruses entering the body. Parasites can cause great damage to human health. If unclear symptoms occur, the possibility of a parasite entering the body should not be excluded, the patient should consult a parasitologist.